Counter App with GTK4 and Rust
GTK and Rust
GTK is a free and open-source cross-platform widget toolkit for creating graphical user interfaces (GUIs).
Rust is a fast, reliable and productive language for building software on embedded devices, web services and more. It is a system programming language focused on safety, speed and concurrency.
Focus of this tutorial is to write a counter app with GTK 4 and Rust.
Project Setup
Let’s begin by installing all necessary tools. First, follow the instructions on the GTK website in order to install GTK 4. Then install Rust with rustup. We are targeting GTK4, Rust 1.75 and gtk-rs version 0.7.3 with features v4_12.
Now lets create a new project by executing:
cargo new gtk4-rust-counter-app
Add gtk4 crate to your dependencies in Cargo.toml.
cargo add gtk4 --rename gtk --features v4_12
Now we can run our application by executing:
cargo run
At this moment it would print Hello, world!.
Application
Lets start by creating GTK Application and connecting to activate event of the Application. We will create a method build_ui to create a window and display it.
use gtk::prelude::*;
use gtk::{glib, Application, ApplicationWindow};
const APP_ID: &str = "org.gtk_rs.GTK4Counter";
fn main() -> glib::ExitCode {
// Create a new application
let app = Application::builder().application_id(APP_ID).build();
// Connect to "activate" signal of `app`
app.connect_activate(build_ui);
// Run the application
app.run()
}
fn build_ui(app: &Application) {
// Create a window and set the title
let window = ApplicationWindow::builder()
.application(app)
.title("GTK Counter App")
.build();
// Present window
window.present();
}
This will dispaly an empty window. Time to add some content.
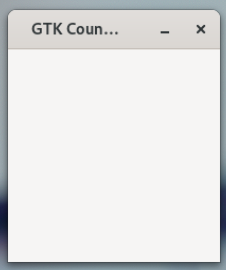
Label
Lets start by adding a Label and displaying Hello World! text. Add Label to gtk imports.
Add following to build_ui method.
let label_counter = Label::builder()
.label("Hello World!")
.margin_top(12)
.margin_bottom(12)
.margin_start(12)
.margin_end(12)
.build();
And add label_counter as child of window.
let window = ApplicationWindow::builder()
.application(app)
.title("GTK Counter App")
.child(&label_counter)
.build();
Running the application now would display Hello World! text in the window.
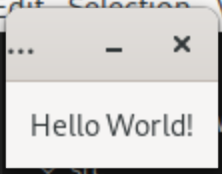
Increment Button
Lets create a button
let button_increase = Button::builder()
.label("Increase")
.margin_top(12)
.margin_bottom(12)
.margin_start(12)
.margin_end(12)
.build();
Now that we have multiple widgets, we would add a gtk_box to hold all the child elements and add that gtk_box as child to window instead.
let gtk_box = Box::builder()
.orientation(Orientation::Vertical)
.build();
gtk_box.append(&label_counter);
gtk_box.append(&button_increase);
...
.child(>k_box)
...
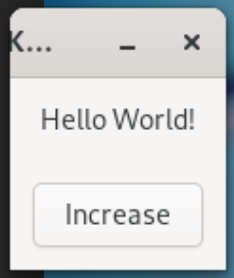
Add Click Handler
Lets add a counter and button click handler. We will update the counter and update the label_counter with the value. Out counter variable would need to be put inside Rc and Cell (not sure if I am using the term correctly) to enable multiple owners and mutable access to variable.
Variable declare will look like following and set label value.
let counter = Rc::new(Cell::new(0));
...
.label(&counter.get().to_string())
...
Lets add a click handler for the button_increase.
button_increase.connect_clicked(clone!(@strong counter, @weak label_counter =>
move |_| {
counter.set(counter.get() + 1);
label_counter.set_label(&counter.get().to_string());
}));
Add Decrease Button and Handler
Lets add another button to decrease the value and update the value
let button_decrease = Button::builder()
.label("Decrease")
.margin_top(12)
.margin_bottom(12)
.margin_start(12)
.margin_end(12)
.build();
button_decrease.connect_clicked(clone!(@weak label_counter =>
move |_| {
counter.set(counter.get() - 1);
label_counter.set_label(&counter.get().to_string());
}));
Source
Source code for the demo application is hosted on GitHub in blog-code-samples repository.
References
In no particular order
- GTK
- GTK Installation
- Rust
- rustup
- gtk-rs
- grk4 crate
- GUI development with Rust and GTK 4
- And many more

Leave a Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *